Delinquency rates on auto loans and credit cards are starting to move higher, in particular in lower income zip-codes (as defined by the Fed), see charts below.
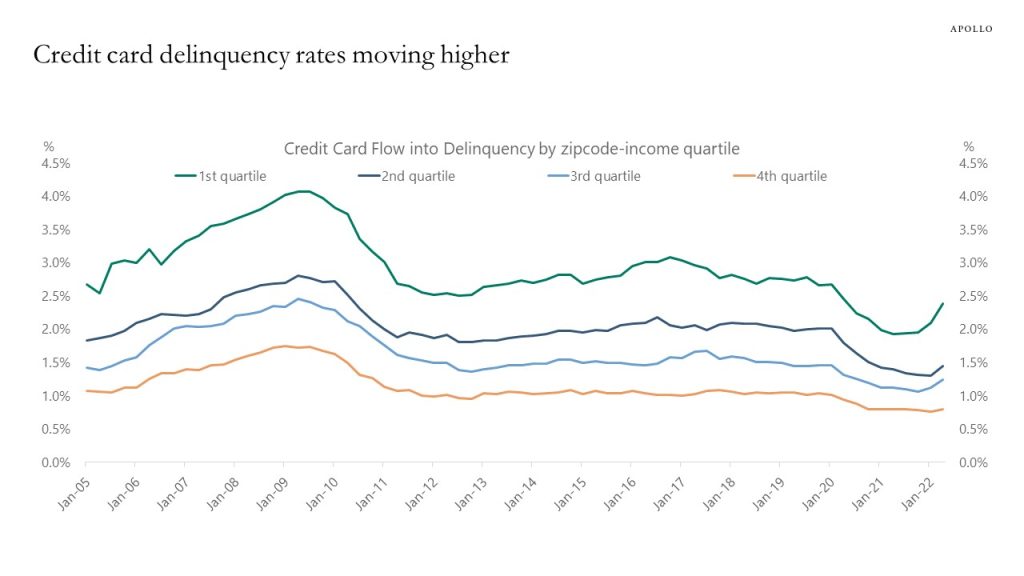
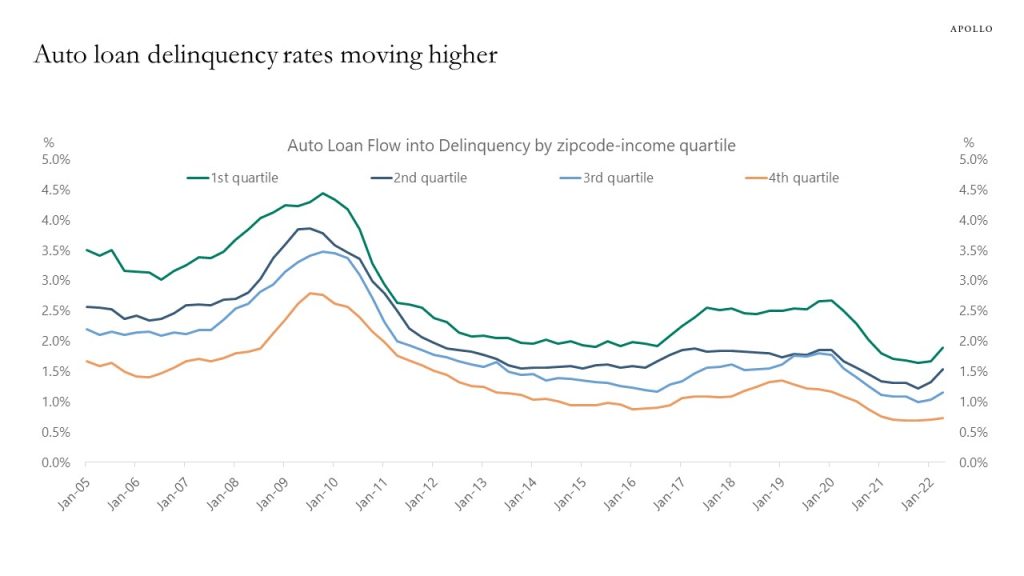


Delinquency rates on auto loans and credit cards are starting to move higher, in particular in lower income zip-codes (as defined by the Fed), see charts below.


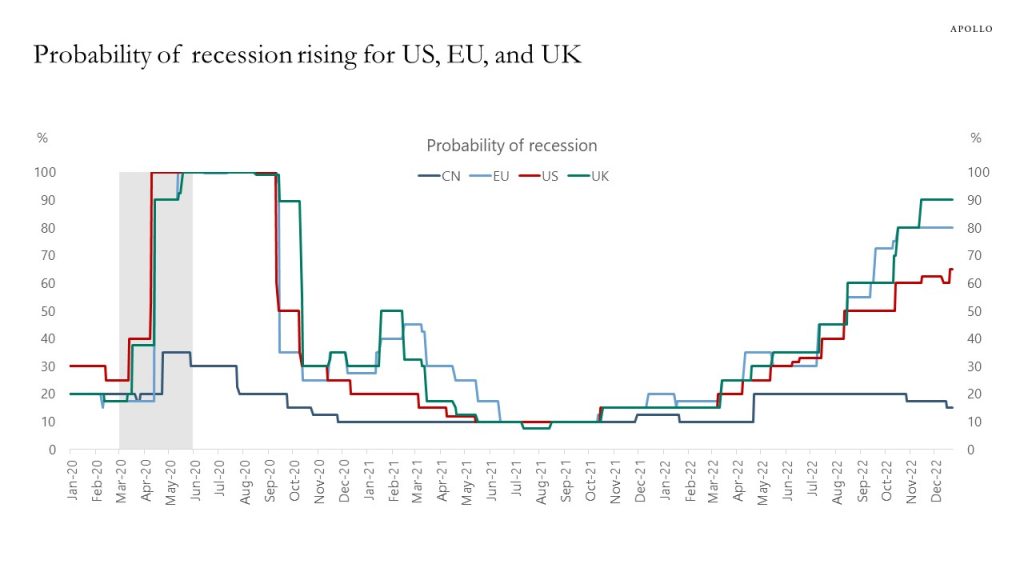
The consensus sees a 90% probability of a recession in the UK and 80% in Europe, and 65% in the US, which continues to point to lower rates in the long end of the curve in 2023.
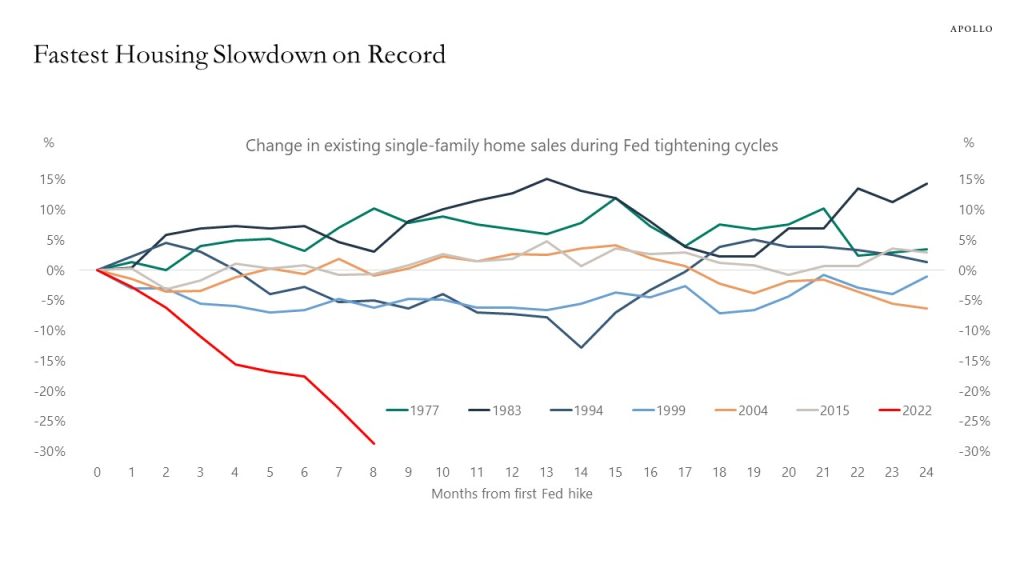
Fed hikes are cooling down the economy and the interest rate-sensitive components of GDP are slowing down (housing, autos, and capex spending), see chart below.
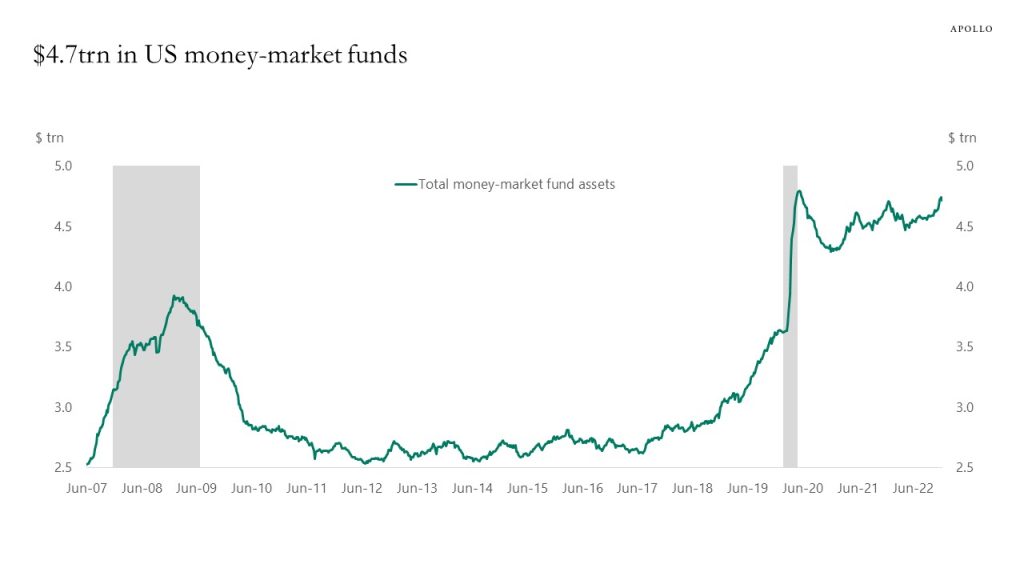
If inflation continues to decline and it becomes clear that we will only get a mild recession, then there is a lot of cash on the sidelines available to be invested in credit markets and equity markets in 2023, see chart below.
Source: Bloomberg, Apollo Chief Economist
This new Fed working paper finds that the monetary policy transmission mechanism has changed in recent years, and the peak impact on the economy now comes after 12 months versus previously 18 months. The argument is that monetary policy no longer only works through the Fed funds rate but also through forward guidance and balance sheet policy.
Have Lags in Monetary Policy Transmission Shortened?
https://www.kansascityfed.org/Economic%20Bulletin/documents/9299/EconomicBulletin22DohFoerster1221.pdf
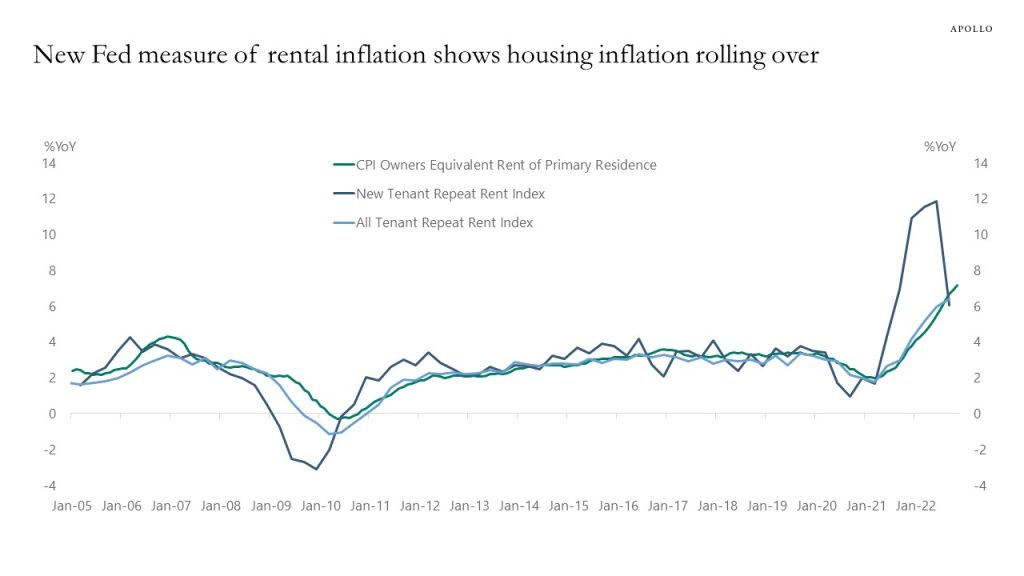
Last week, the Fed published a new working paper calculating a new measure of rent inflation using only newly signed leases, and it shows that housing inflation has rolled over, see chart below. As Fed Chair Powell has pointed out, we should also expect to see the same profile in the housing components of the CPI.
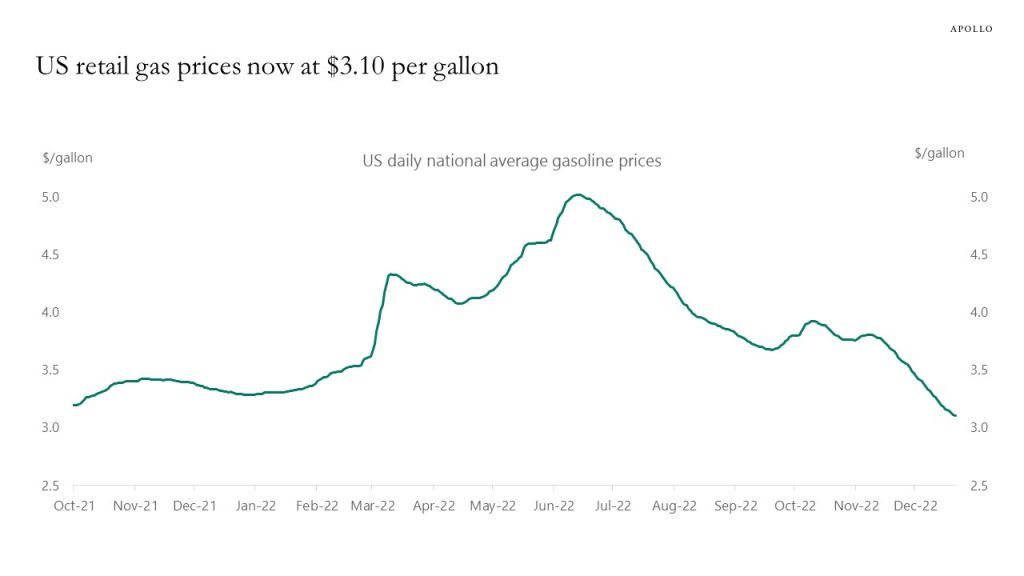
US retail gas prices continue to decline and are now lower than before Russia invaded Ukraine, driven by slowing global growth and the release from the Strategic Petroleum Reserve. The main upside risk to global growth and inflation going into 2023 is China’s reopening, which could lift oil prices and complicate the Fed’s efforts at getting inflation back to 2%.
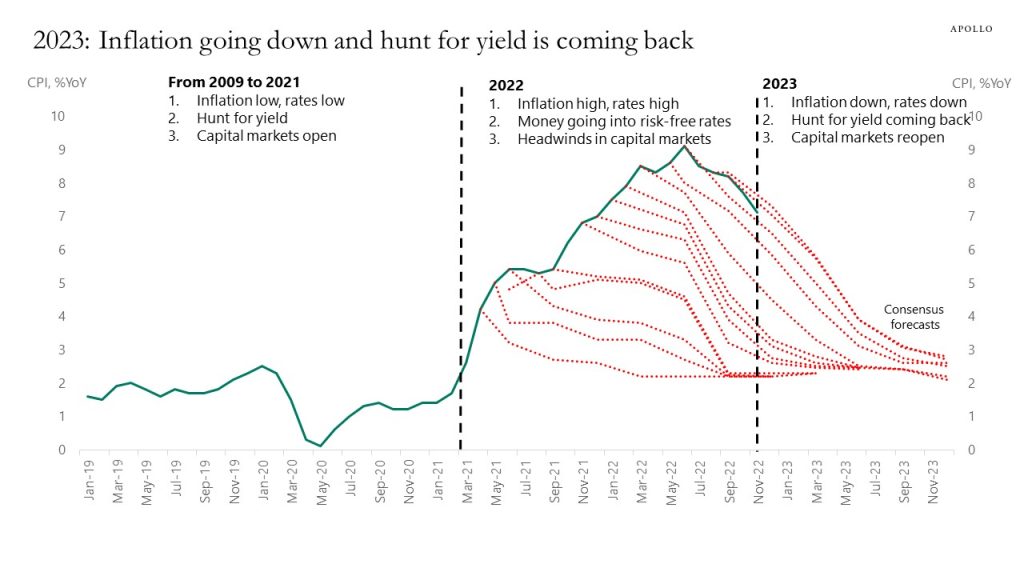
From 2009 to 2022 inflation was low, rates were low, capital markets were open, and the optimal strategy for investors was to hunt yield.
In 2022 inflation became a problem, and the Fed reacted and raised rates, and capital markets became more challenging, and investors sold credit and equities and put money into rising risk-free rates.
Because of cumulative Fed action, inflation is coming down in 2023 and rates will be coming down and the hunt for yield will be coming back and capital markets will reopen.
The bottom line is that the ongoing covid-driven inflation shock has lasted longer than the Fed and the market initially expected, but the Fed’s commitment to low inflation is why the inflation problem in 2022 will turn out to be transitory. Investors should appreciate that we in 2023 are transitioning back to low inflation again, and the optimal asset allocation strategy in 2023 is likely to be the opposite of what worked in 2022. I discuss this in more detail in our 2023 outlook report and 45-minute video here on ApolloAcademy.com.
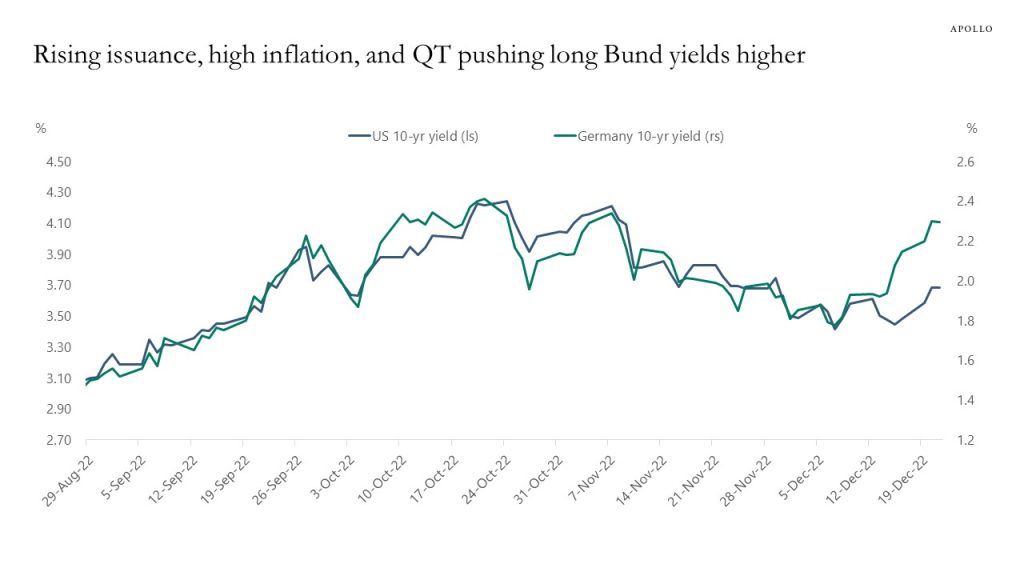
Government bond yields in Europe have over the past week started to decouple from US Treasury yields, driven by rising government spending in Europe, high inflation in Europe, and ECB QT.
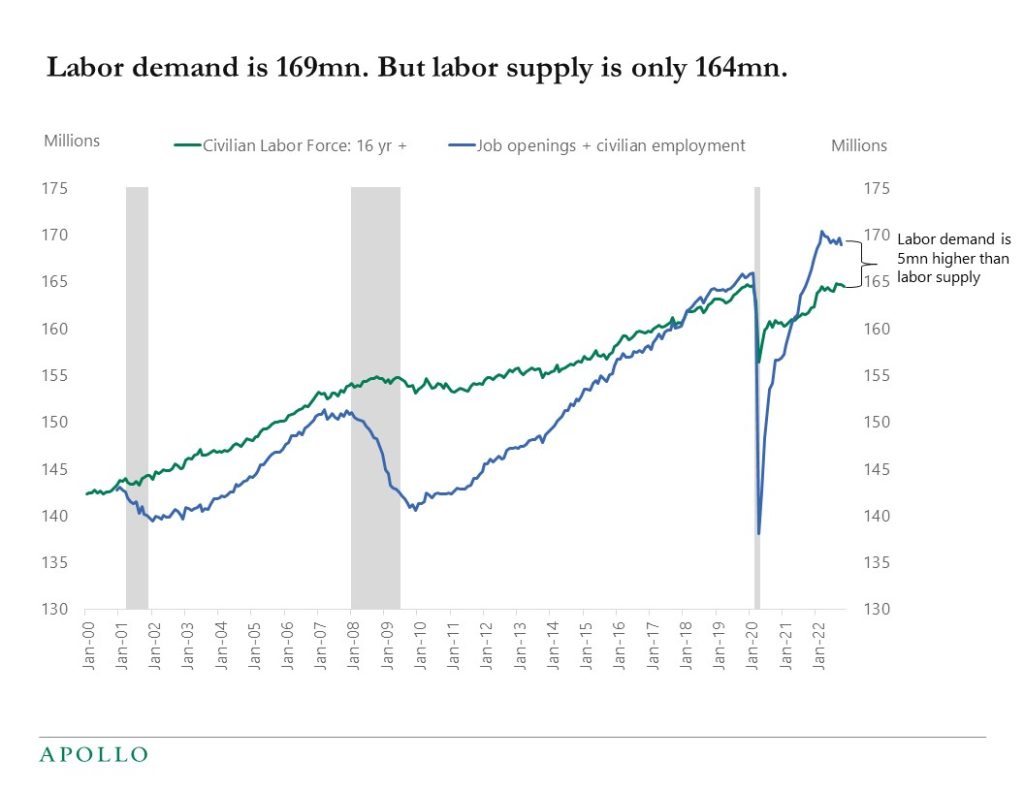
The chart below is the reason why Fed Chair Powell talks so much about the tight labor market. There are 164 million people in the US labor force. And total labor demand is 169 million (defined as total employment plus the total number of job openings). In other words, labor demand is 5 million people higher than labor supply, which is why wage inflation is so strong. The solution to this imbalance is to either increase the labor supply, for example through higher immigration, or to lower labor demand for example through an increase in the unemployment rate, and this is the challenge for the Fed.